Abstract
Deep molecular response in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukaemia (CP-CML) is associated with superior event free survival, provides a platform for treatment free remission and is increasingly being adopted as a goal of therapy. Interferon was a commonly used CML therapy in the pre-imatinib era, exerting direct anti-leukemic activity and immune-stimulatory properties. Combining interferon and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) may lead to synergistic anti-leukemic effects. We report the interim analysis of the Pinnacle phase II study, combining nilotinib with pegylated interferon alfa-2B (Peg-IFN) in CP-CML, evaluating tolerability of the combination and efficacy as measured by molecular responses.
All patients received nilotinib 300mg BID for the first 3 months (mths). Peg-IFN (PegIntron, MSD) was added at 30mcg/week in the 4th mth in patients without persistent haematological toxicities, increasing to 50mcg/week as tolerated over the following mth. Combination therapy continued until 24 mths, when patients reverted to TKI monotherapy. Switching to imatinib 400-600mg QD was allowed for patients with persistent grade II or any grade III/IV toxicity from nilotinib. The co-primary end points are MR4.5 (BCR-ABL1 ≤0.0032% IS) at 24 mths and MMR (BCR-ABL1 ≤0.1% IS) at 12 mths. Patients were screened for cardiac / vascular disease and associated risk factors at baseline (EKG, ejection fraction via ultrasound or nuclear med, arterial duplex of carotids and lower limbs, blood HbA1c and lipid profiles). Patients with uncontrolled vascular risk factors (diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia) or a history of vascular events were excluded.
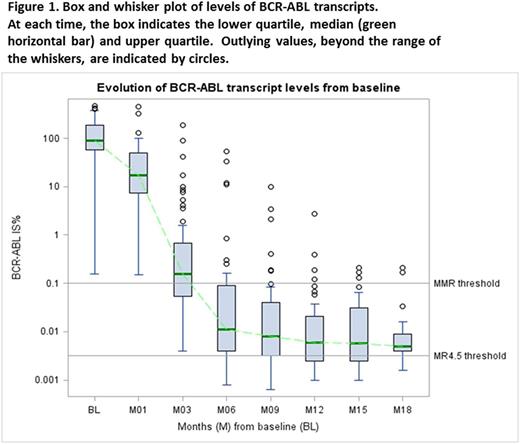
Sixty patients were recruited from 12 Australian centres. Median age was 48.5 years (range 19-72), and 45% were female. Sokal risk was low in 43% and high in 18%. Median follow up was 14 mths (2.4-37). Figure 1 shows BCR-ABL1 transcript levels over time. Of the 59 patients followed up for ≥3 mths, 5 had BCR-ABL1 >10% at 3 mths (8.5%). Two patients lost MMR whilst on study - one associated with nilotinib interruption due to toxicity.
This protocol-specified interim analysis of the co-primary endpoint, MMR at 12 mths, used the method of repeated confidence intervals (CI) and a pre-specified alpha-spending function. In 33 evaluable patients with >12 mths follow up, the MMR rate at 12 mths was 76% (99.5% CI 50-93%), and MR4.5 rate 42% (99.5% CI 20-68%). One patient transformed to blast crisis 1 mth after discontinuing therapy after 9 mths of study therapy.
Dose intensities of nilotinib and peg-IFN were assessed in 3 mth blocks in patients receiving these therapies. Median nilotinib dose intensity was 600mg/d during mths 0-3, 3-6, 7-9 and 10-12. The most common grade III/IV adverse events (AE) attributed to nilotinib were increased lipase (12%), neutropenia (15%), and each at 6%: pancreatitis, hypertriglyceridemia and thrombocytopenia. The most common grade III/IV adverse events (AE) attributed to peg-IFN were neutropenia (14%), and each at 4%: fatigue, hyperthyroidism and thrombocytopenia. Of the 52 patients still on study, 43 (83%) are on nilotinib and 9 (17%) on imatinib. Only one ischaemic vascular event occurred: ischemic colitis 5 mths after switching from nilotinib to imatinib for elevated pancreatic and hepatic enzymes.
Median dose intensity of Peg-IFN during mths 4-6 of study was 44mcg/week (range 19-50), 50mcg/week during mths 7-9 and 10-12 (range 15-50 and 10-50 respectively). Median duration of Peg-IFN exposure at this time is 13.4 mths (range 1-21). Eleven patients completed assigned Peg-IFN treatment (10 on full dose), 8 are receiving ongoing treatment (4 on <50mcg/week), 5 never started Peg-IFN and 9 stopped the drug due to thyroid disorders (n=3), and 1 each from dyslipidaemia /pancreatitis, rash, depression, fatigue, protocol violation and inefficacy. Two stopped within 3 mths of starting, 2 between mths 4-6, 3 between mths 7-12 and 2 between mths 13-18.
Eight patients (13%) have withdrawn from study: 2 for treatment failure, 4 from toxicity (3 for pancreatitis, 1 for liver enzyme derangements), and 2 withdrew consent. No death has been reported on or off study.
This interim analysis suggests that combination therapy with nilotinib and Peg-IFN has an acceptable toxicity profile and that co-administration does not compromise TKI dose intensity. Observed 12 mth rates of MMR and MR4.5 compare favourably with other nilotinib monotherapy trials.
Yeung: BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Honoraria, Research Funding. Grigg: Roche: Other: Funding to attend ASH 2016. Shanmuganathan: Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Travel Support; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Other: Travel Support. Mills: Novartis: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Specialised Therapeutics: Honoraria. Schwarer: Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Specialised Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Yong: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. White: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Branford: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Qiagen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Ariad: Honoraria, Research Funding; Otsuka: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Hughes: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal